IADR Abstract Archives
Fibroma – The Necessity to Biopsy?
Objectives: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the necessity for biopsy and histological examinaton of tissue removed from the oral cavity when the clinical impression undoubtedly indicates a benign lesion. Specifically, is it necessasry to submit excised fibromas for histological examination?
Methods: Records were extracted from the VCU Oral Pathology biopsy service database containing 168,095 cases biopsied from late 1987 through April 2011. Variables of interest queried included clinical impression of contributor, diagnosis by oral pathologist, location, date, contributor's practice type, patient's sex, DOB and age. For this specific project the clinical impression of the contributing doctor containing the word "fibroma" was selected. Data extraction was accomplished using Microsoft Access 2010. Analysis included bivariate ANOVA and repeated measures of logistic regression and was completed using JMP Pro 11.0.0, and SAS 9.4, SAS OInstitute Inc., Cary, NC, USA.
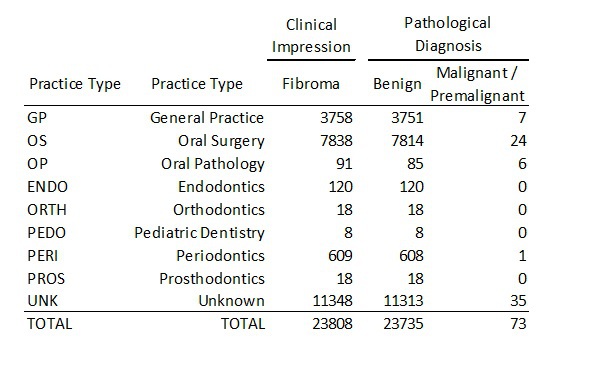
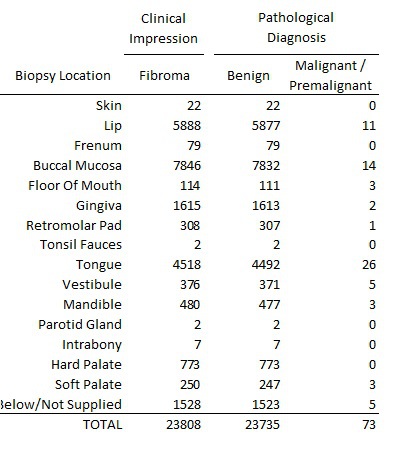
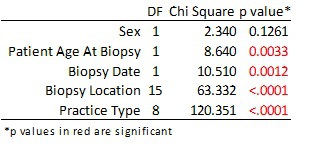
Results: The data set contained 23,808 patients with clinical impression "Fibroma". Histological diagnosis included multiple unique findings, which when collapsed into "Benign" and "Malignant/Premalignant" yielded 23,735 (99.7%) benign and 73 (0.3%) malignant/premalignant lesions including: adenoid cystic carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and epithelial dysplasia (mild, moderate and severe). Bivariate analysis of possible predictor variables found Patient Age at Biopsy, Biopsy Location, and Practice type to be significant (p<0.05).
Conclusions: While the number of malignant and premalignant lesions in this very large series of biopsies is extremely small, it nonetheless demonstrates that a clinician cannot assume the biological nature of the excised lesion to be benign and therefore choose not to submit the specimen for histological analysis.
Methods: Records were extracted from the VCU Oral Pathology biopsy service database containing 168,095 cases biopsied from late 1987 through April 2011. Variables of interest queried included clinical impression of contributor, diagnosis by oral pathologist, location, date, contributor's practice type, patient's sex, DOB and age. For this specific project the clinical impression of the contributing doctor containing the word "fibroma" was selected. Data extraction was accomplished using Microsoft Access 2010. Analysis included bivariate ANOVA and repeated measures of logistic regression and was completed using JMP Pro 11.0.0, and SAS 9.4, SAS OInstitute Inc., Cary, NC, USA.
Results: The data set contained 23,808 patients with clinical impression "Fibroma". Histological diagnosis included multiple unique findings, which when collapsed into "Benign" and "Malignant/Premalignant" yielded 23,735 (99.7%) benign and 73 (0.3%) malignant/premalignant lesions including: adenoid cystic carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and epithelial dysplasia (mild, moderate and severe). Bivariate analysis of possible predictor variables found Patient Age at Biopsy, Biopsy Location, and Practice type to be significant (p<0.05).
Conclusions: While the number of malignant and premalignant lesions in this very large series of biopsies is extremely small, it nonetheless demonstrates that a clinician cannot assume the biological nature of the excised lesion to be benign and therefore choose not to submit the specimen for histological analysis.