IADR Abstract Archives
Radiographic Study Analysis of the Prevalence of Dental Anomalies in Patients With Cleft Lip and/or Palate
Objectives: Identify dental anomalies in patients with the different types of Cleft Lip and Palate treated at Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino Jesus(HMIMJ), located in the city of São Paulo, in the period from 2013 to 2014 by analyses of photograph and radiograph data of a group of patients to investigate the prevalence of dental anomalies according to the different types of cleft.
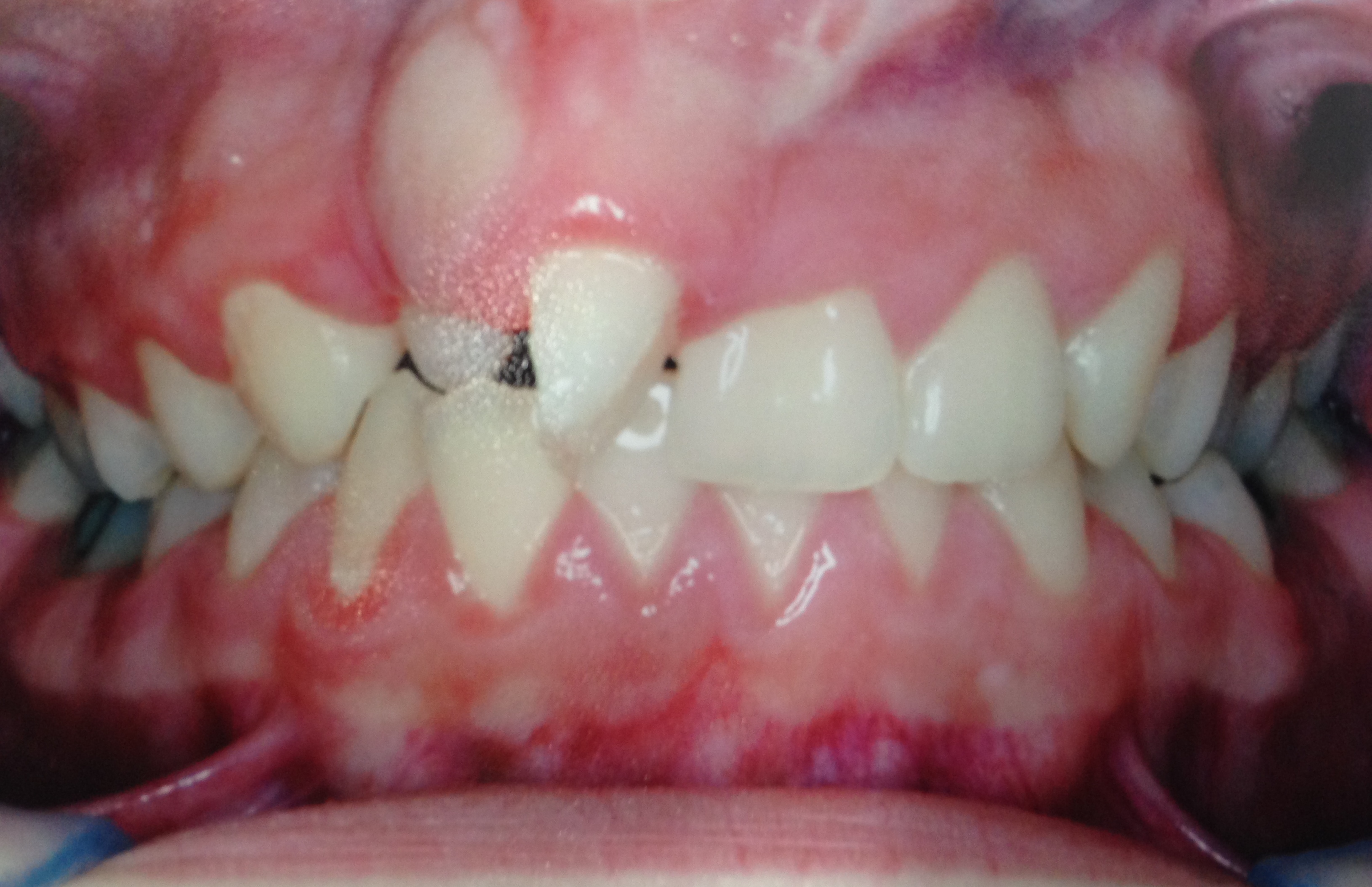
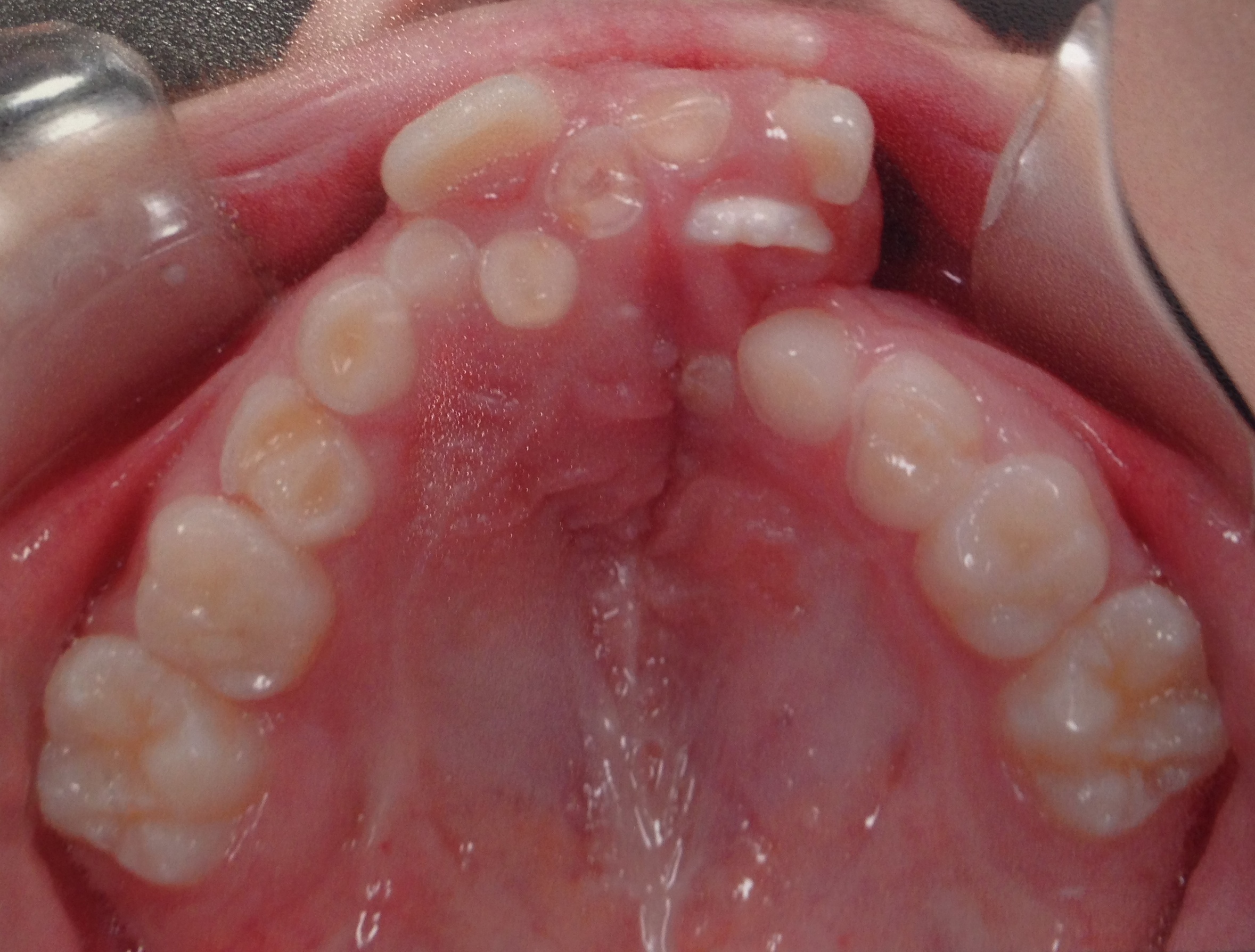
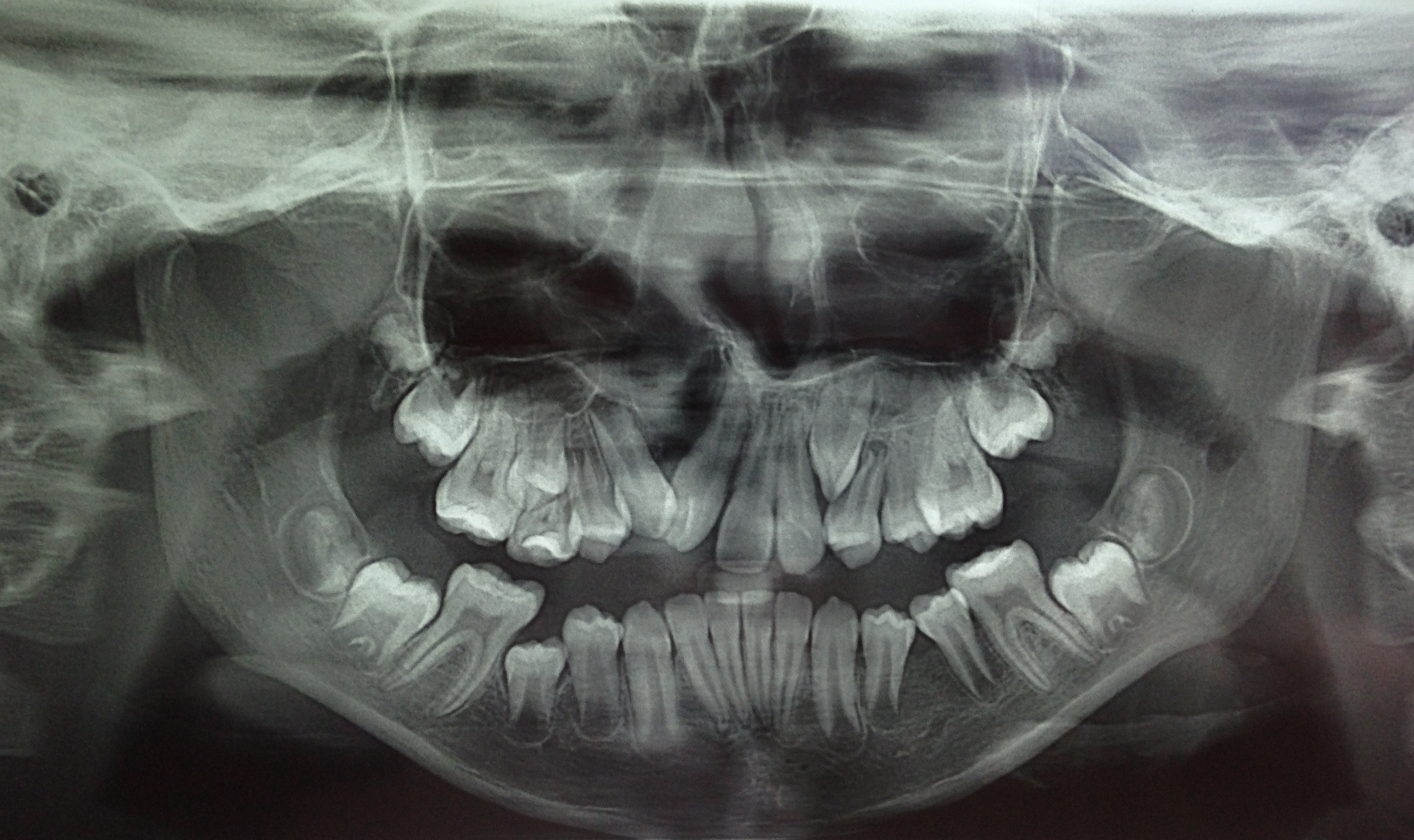
Methods: A cross sectional study was performed in the Department of Dentistry at the Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino Jesus (HMIMJ), in São Paulo, Brazil, with 75 patients between 06 and 18 years old, treated from 2013 to 2014. Therefore, we used photos and panoramic radiographs present in the clinical records of the cleft lip and/or cleft palate’ patients, investigating the presence of dental abnormalities according to the types of cleft.
Results: Dental anomalies were frequently identified in patients with cleft lip and/ or cleft palate. The majority (81,3%) of the examined had at least one kind of dental abnormality. Tooth agenesis is the most frequent (61,3%), and among this category, the lateral incisor were the most affected (86,3%). Has yet been identified at the analyses, patients with impacted teeth (20%), tooth rotations (29.3% ), with crown/root hypoplasia (13.3%) and root deviation (5.3%).
Conclusions: This study shows the high prevalence of dental anomalies present in patients with CL/P treated at HMIMJ, between 2013 and 2014. Dental anomalies were observed in 81,3% of patients. It was also demonstrated that patients only with cleft palate (post-foramen incisor) are the ones with fewer dental abnormalities (20% of the patients with this kind of cleft). The highest presence of dental anomalies was observed in the cleft lip and palate group. So it is suggested that during the treatment planning of patients with cleft lip and palate, panoramic radiographs are implemented during the mixed dentition as routine dental resource for identifying these anomalies, as well as implementing the planning of surgical / orthodontic / dental treatment of these patients.
Methods: A cross sectional study was performed in the Department of Dentistry at the Hospital Municipal Infantil Menino Jesus (HMIMJ), in São Paulo, Brazil, with 75 patients between 06 and 18 years old, treated from 2013 to 2014. Therefore, we used photos and panoramic radiographs present in the clinical records of the cleft lip and/or cleft palate’ patients, investigating the presence of dental abnormalities according to the types of cleft.
Results: Dental anomalies were frequently identified in patients with cleft lip and/ or cleft palate. The majority (81,3%) of the examined had at least one kind of dental abnormality. Tooth agenesis is the most frequent (61,3%), and among this category, the lateral incisor were the most affected (86,3%). Has yet been identified at the analyses, patients with impacted teeth (20%), tooth rotations (29.3% ), with crown/root hypoplasia (13.3%) and root deviation (5.3%).
Conclusions: This study shows the high prevalence of dental anomalies present in patients with CL/P treated at HMIMJ, between 2013 and 2014. Dental anomalies were observed in 81,3% of patients. It was also demonstrated that patients only with cleft palate (post-foramen incisor) are the ones with fewer dental abnormalities (20% of the patients with this kind of cleft). The highest presence of dental anomalies was observed in the cleft lip and palate group. So it is suggested that during the treatment planning of patients with cleft lip and palate, panoramic radiographs are implemented during the mixed dentition as routine dental resource for identifying these anomalies, as well as implementing the planning of surgical / orthodontic / dental treatment of these patients.