IADR Abstract Archives
Ki-67 PROLIFERATIVE INDEX IN ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS – A BETTER PREDICTION OF NEOPLASTIC POTENTIAL
Objectives: Odontogenic keratocysts (OKCs) are common and clinically aggressive lesions. World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends the term keratocystic odontogenic tumour (KOT) reflecting its neoplastic nature. Ki-67 is a well-known marker for cell proliferation and its expression increases with high cell turn over particularly in pre-malignant and malignant lesions of the oral mucosa. This study was, therefore, designed to determine the Ki-67 labelling index in OKCs to assess their neoplastic potential.
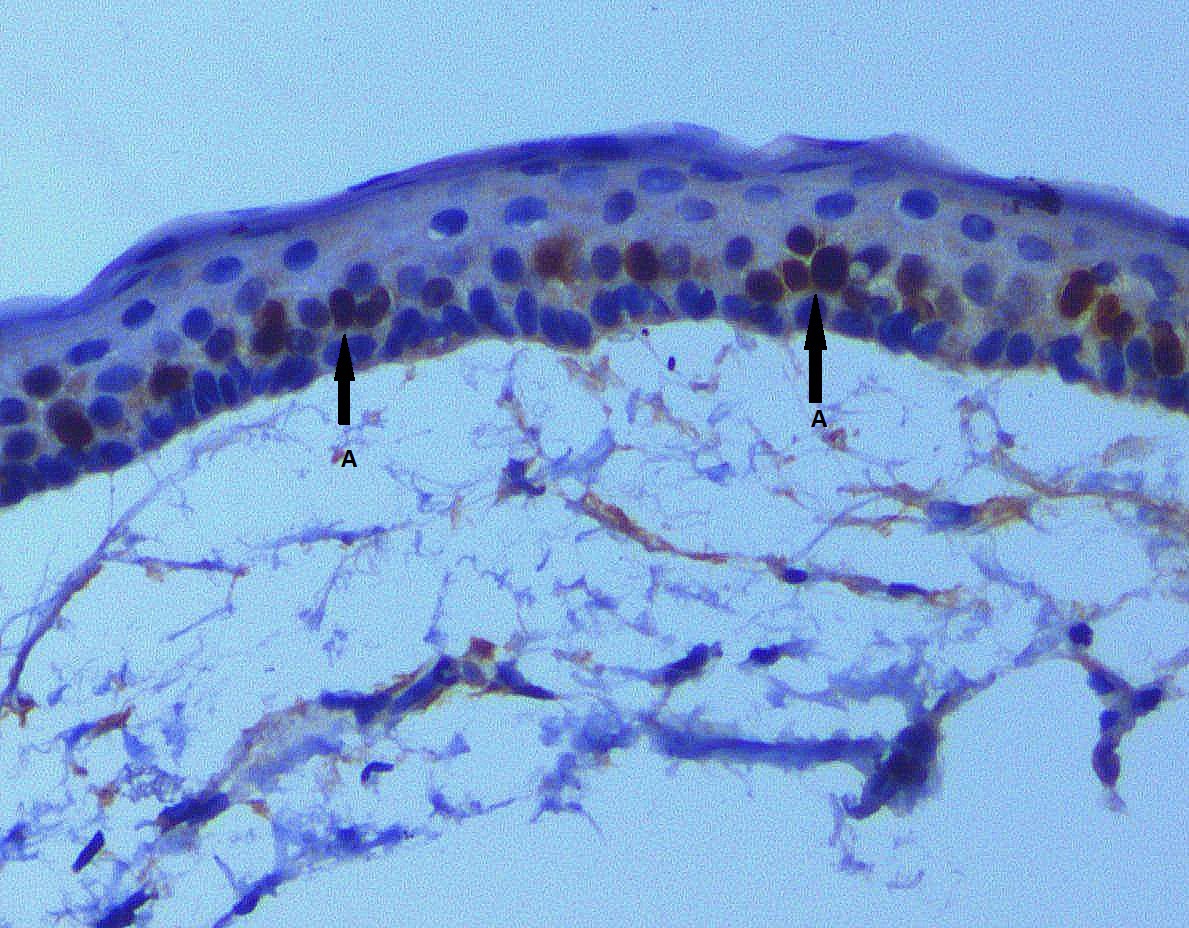
Methods: Biopsies were taken from n=40 study subjects presenting with radiolucent lesions of the jaw. A total of n=15 biopsies were histologically diagnosed as OKCs. Ki-67 proliferative index with nuclear positivity of epithelial cells was categorized as negative (< 5%), low (5-50%) and high (>50%) using MIB-1 immunohistochemistry.
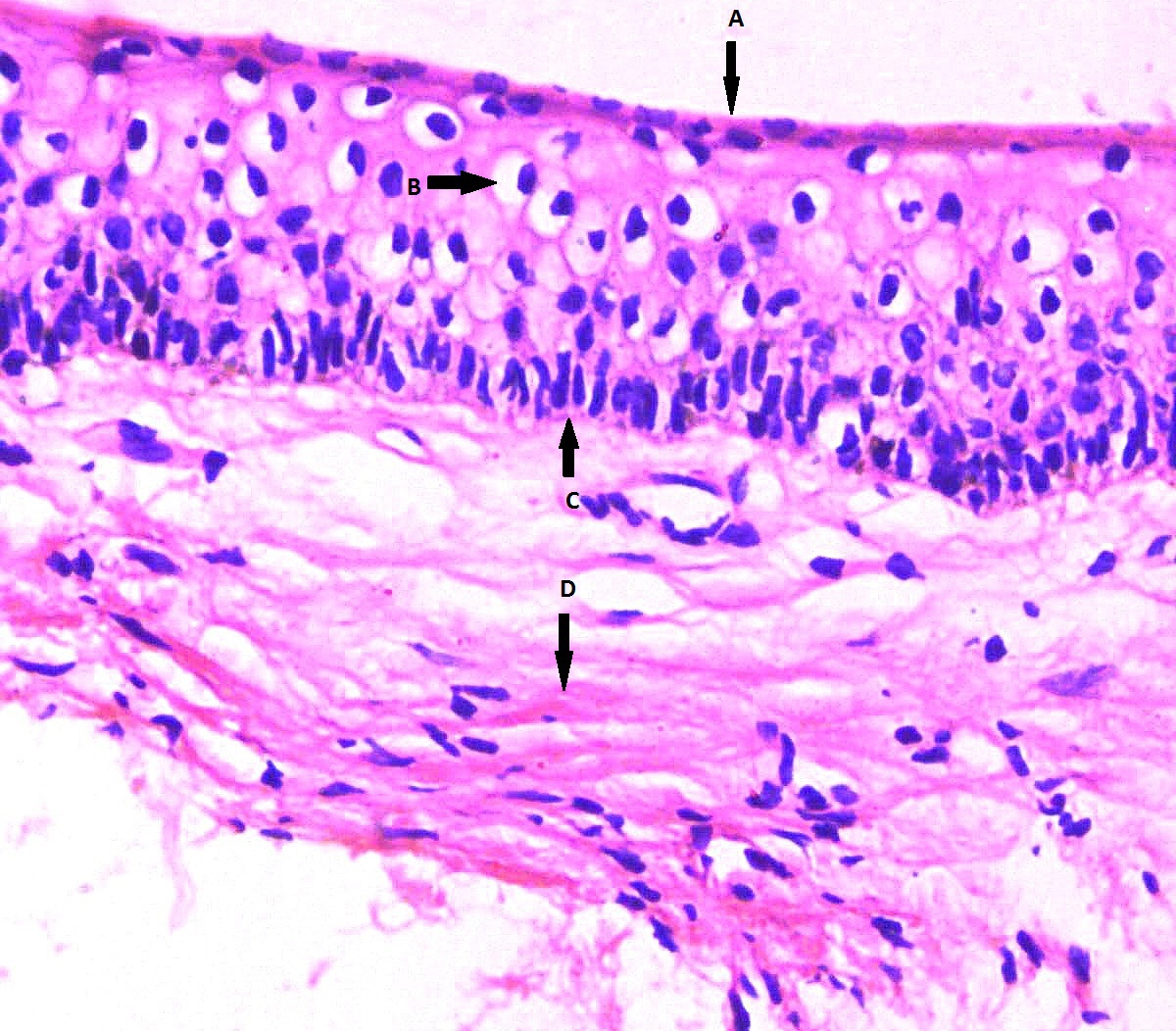
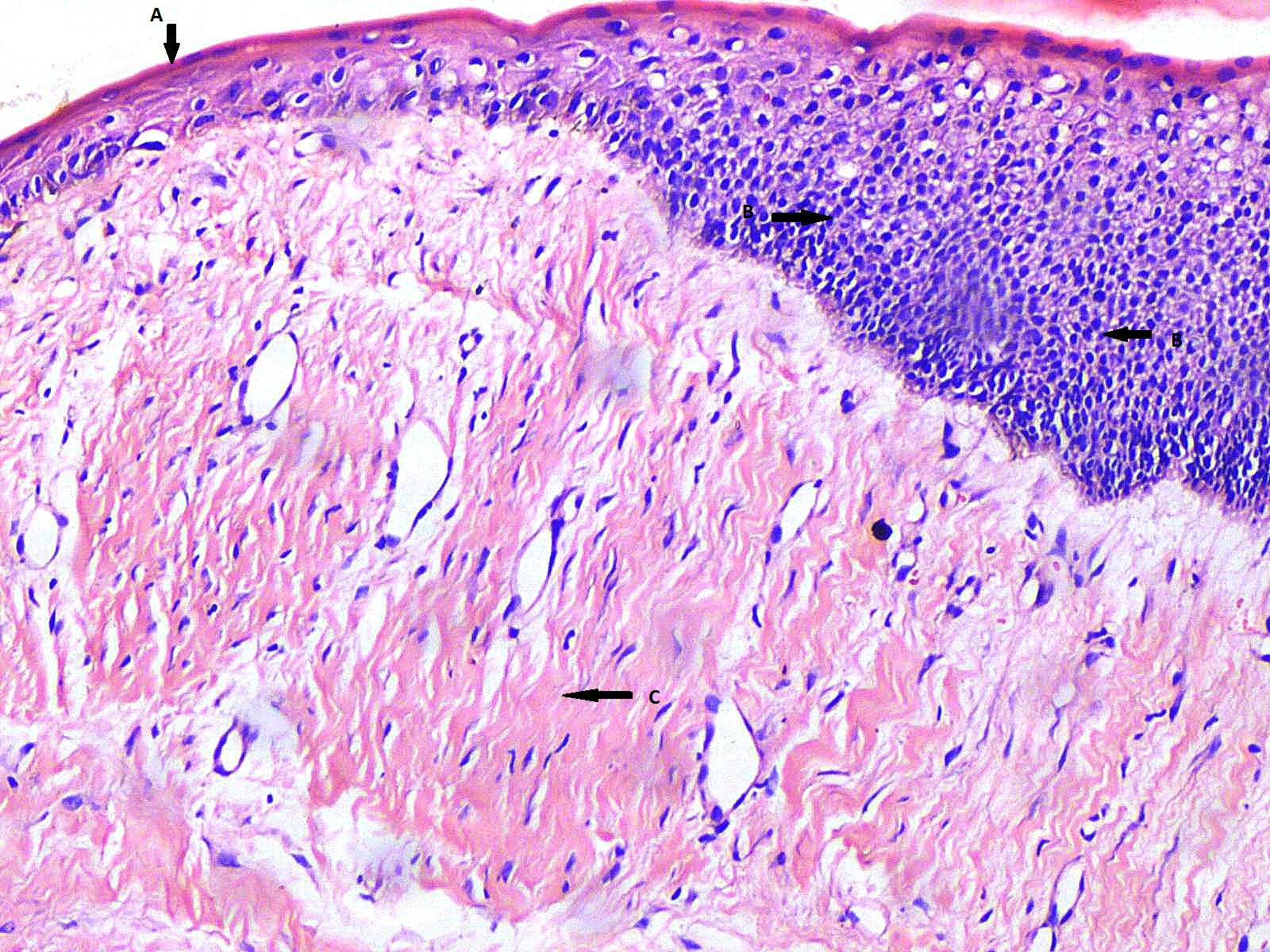
Results: Mean age of patients was 30.6 ± 14.5 years with a male to female ratio being 2:1. Painless swelling was the most frequently reported symptom (61.5%). Radiographically, 69.2% of OKCs were < 2cm in diameter. Posterior mandible was the commonest site (61.5%) and 92.3% of the cysts were unilocular. Histologically, 61.5% and 30.8% of OKCs demonstrated parakeratinized and nonkeratinized epithelium respectively. Epithelial hyperplasia (38.5%), keratinocytic spongiosis (46.2%), acantholysis (7.7%) and epithelial atypia (84.6%) with mild nuclear pleomorphism (76.9%), loss of polarity (92.3%) and prominent nucleoli (46.2%) were observed. Stroma showed fibroplasia (76.9%), chronic inflammation (76.9%) of moderate degree (53.8%) and vascular congestion (15.4%). Negative (15.4%), low (76.9%) and high (7.7%) Ki-67 index within the keratinocytic nuclei was observed. Foci having epithelial atypia demonstrated stronger staining intensity compared to adjacent normal epithelium. However, no significant association was observed between the histological variables and Ki-67 labelling.
Conclusions: Based on re-classification of OKC to keratocystic tumour, high labelling index and stronger intensity of Ki-67 staining may reliably predict neoplastic, locally aggressive and recurrence potential of these cysts. Large scale follow up study is suggested in future.
Methods: Biopsies were taken from n=40 study subjects presenting with radiolucent lesions of the jaw. A total of n=15 biopsies were histologically diagnosed as OKCs. Ki-67 proliferative index with nuclear positivity of epithelial cells was categorized as negative (< 5%), low (5-50%) and high (>50%) using MIB-1 immunohistochemistry.
Results: Mean age of patients was 30.6 ± 14.5 years with a male to female ratio being 2:1. Painless swelling was the most frequently reported symptom (61.5%). Radiographically, 69.2% of OKCs were < 2cm in diameter. Posterior mandible was the commonest site (61.5%) and 92.3% of the cysts were unilocular. Histologically, 61.5% and 30.8% of OKCs demonstrated parakeratinized and nonkeratinized epithelium respectively. Epithelial hyperplasia (38.5%), keratinocytic spongiosis (46.2%), acantholysis (7.7%) and epithelial atypia (84.6%) with mild nuclear pleomorphism (76.9%), loss of polarity (92.3%) and prominent nucleoli (46.2%) were observed. Stroma showed fibroplasia (76.9%), chronic inflammation (76.9%) of moderate degree (53.8%) and vascular congestion (15.4%). Negative (15.4%), low (76.9%) and high (7.7%) Ki-67 index within the keratinocytic nuclei was observed. Foci having epithelial atypia demonstrated stronger staining intensity compared to adjacent normal epithelium. However, no significant association was observed between the histological variables and Ki-67 labelling.
Conclusions: Based on re-classification of OKC to keratocystic tumour, high labelling index and stronger intensity of Ki-67 staining may reliably predict neoplastic, locally aggressive and recurrence potential of these cysts. Large scale follow up study is suggested in future.